Alzheimer
Alzheimer’s disease is a progressive neurodegenerative disease that affects cognitive functions such as memory, thought, and behaviour. It is the most common form of dementia in older adults. As the disease progresses, it causes changes in the brain, including the loss of connections between nerve cells and eventually the death of these cells.
Individuals diagnosed with Alzheimer’s experience changes in behaviour and personality traits, along with a gradual loss of memory and cognitive ability. These factors impair their ability to interact naturally or perform daily tasks.
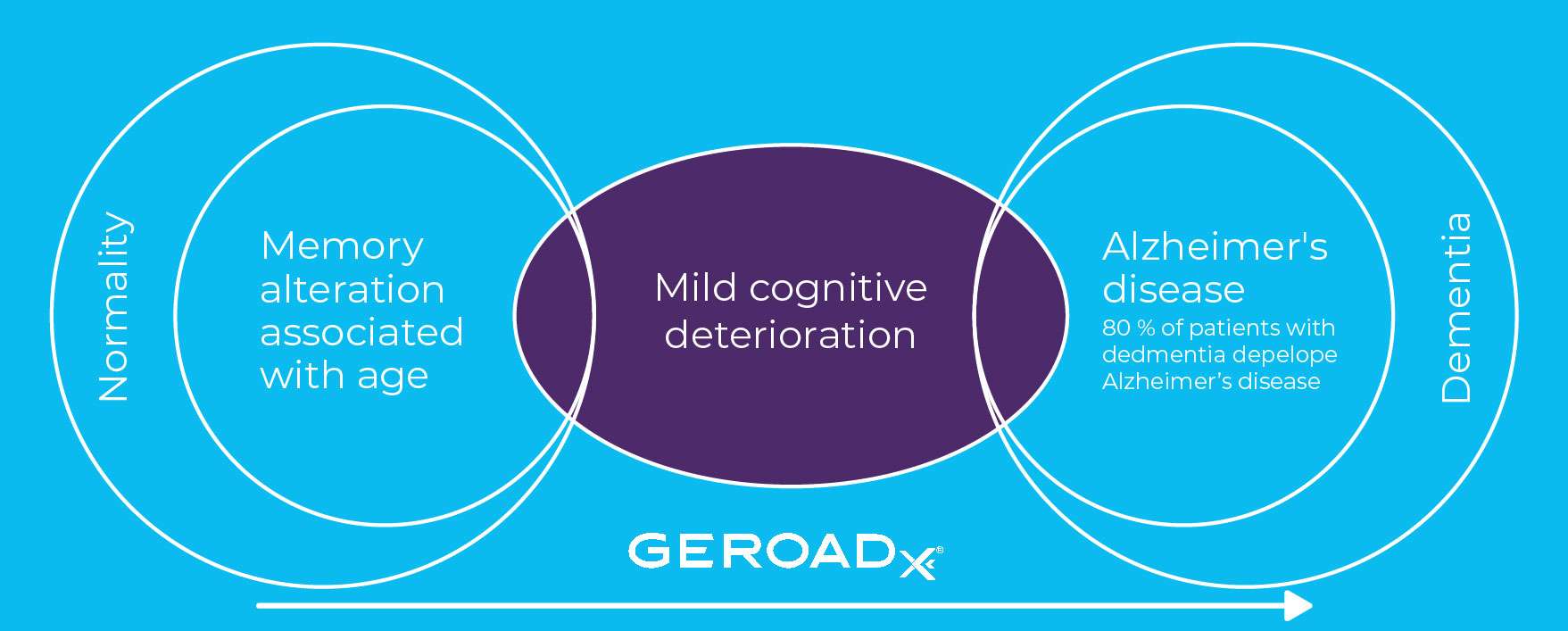
- Mild Cognitive Impairment can, in turn, progress to Alzheimer's disease.
- GEROADx's salivary biomarker is a very useful tool in the diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease and associated Mild Cognitive Impairment.
RISK FACTORS ASSOCIATED WITH ALZHEIMER'S
- Age Alzheimer's disease, as a neurodegenerative condition, increases with age, and its first symptoms appear later in life.
- Family HistoryIndividuals with a family history of Alzheimer's due to genetic factors have a higher risk of developing the disease.
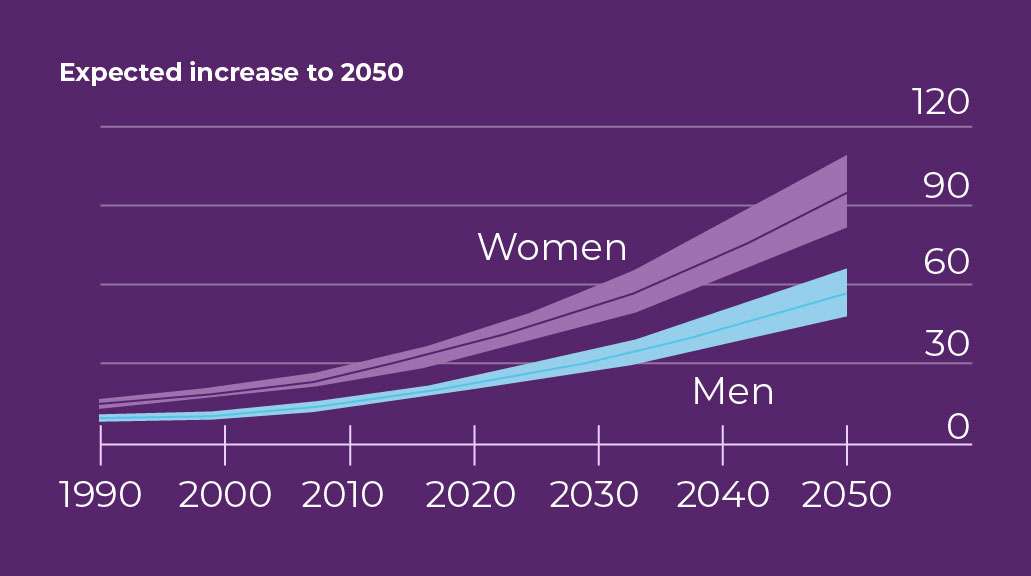
- GenderWomen are more likely to develop Alzheimer's disease than men. According to the WHO, 65% of deaths from Alzheimer's and other forms of dementia occur in women. From data in England and Wales we know that this is not only a morbidity issue but also a mortality issue.
- Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI)Individuals with Mild Cognitive Impairment have a higher risk of developing Alzheimer's disease.
- Cardiovascular and Metabolic HealthFactors such as high blood pressure, diabetes, obesity and high cholesterol can contribute to the development of Alzheimer's disease.
- Lifestyle FactorsLack of physical activity, poor diet, smoking, alcohol consumption, and limited social interaction can increase the risk of developing the disease.
- Sleep Disorders and Apnea Individuals with these disorders are more likely to develop Alzheimer's disease.
- Hearing LossIndividuals with adult-onset hearing loss are more likely to develop Alzheimer's disease.
Prevalence of Alzheimer's disease
in the global population
Expected increase to 2050
THE ALZHEIMER TSUNAMI
- According to PAHO (Pan American Health Organization), 10 million people in the Americas are living with dementia, 80% of whom will develop Alzheimer's Disease.
- The populations of Latin America and the Caribbean will be the most affected, with 7.6 million people suffering from dementia by 2030.
- In 2022, Alzheimer's Disease became the leading cause of death in England and Wales.
- Most Alzheimer's Disease diagnoses are associated with modifiable risk factors, with only 5% to 10% known to be associated with genetic factors.
- Approximately 70% of dementia cases are due to Alzheimer's disease.
- By 2030, more than half of Alzheimer's Disease diagnosis in the United States will be in the Latino and African American populations.
THERAPIES AND TREATMENTS
Once diagnosed by a neurologist, available treatments and therapies are evaluated. These treatments and therapies tend to be more effective when the patient receives an early diagnosis. Although there is currently no cure for Alzheimer’s Disease, there are therapeutic options that can delay symptom progression and improve the quality of life for both the patient and their caregivers.
Today, there are several available strategies:
- Pharmacological treatments, which can be symptomatic or disease-modifying.
- Lifestyle-based treatments, including physical exercise, nutrition and cognitive therapy, among others.
- Treatments that target risk factors such as obesity, diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, among others.